
Generative AI in the Enterprise: Strategic Considerations for CTOs
Introduction
Six months ago, ChatGPT crossed 100 million users faster than any technology in history. Since then, the generative AI landscape has evolved rapidly. GPT-4 launched in March with dramatically improved capabilities. Google responded with Bard. Microsoft integrated AI across its product suite. Every major technology vendor now has a generative AI story.
For enterprise CTOs, the question is no longer whether generative AI matters—it clearly does. The question is how to capture value while managing very real risks. This requires moving beyond experimentation toward strategic deployment.
The Current Landscape
Available Capabilities
As of mid-2023, enterprise leaders have several options:
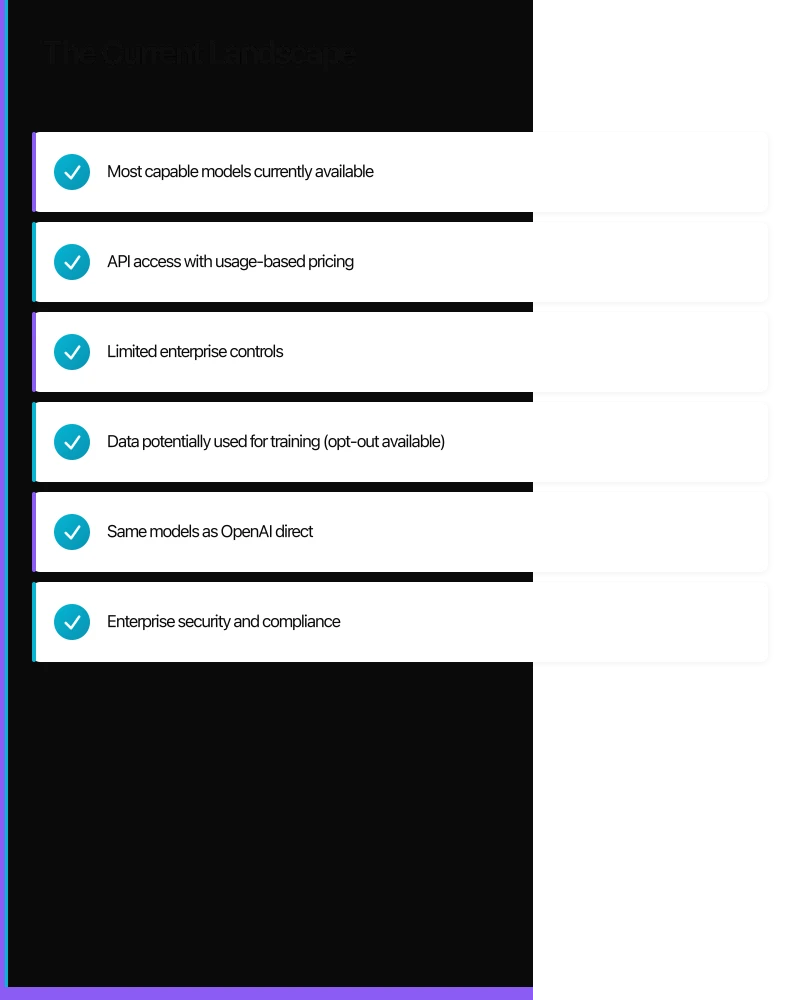
OpenAI Direct
GPT-4 and GPT-3.5 via API:
- Most capable models currently available
- API access with usage-based pricing
- Limited enterprise controls
- Data potentially used for training (opt-out available)
Azure OpenAI Service
Microsoft’s enterprise deployment of OpenAI models:
- Same models as OpenAI direct
- Enterprise security and compliance
- Data stays within Azure boundary
- Virtual network integration
- Generally available since January 2023
Google Cloud
Bard and PaLM models:
- Competitive capabilities emerging
- Strong Google Cloud integration
- Vertex AI platform for deployment
- Still maturing for enterprise use
Amazon Web Services
Bedrock (currently in preview):
- Multiple model providers planned
- AWS integration and security
- Expected general availability later this year
- Foundation for AWS AI strategy
Enterprise Adoption Patterns
Early enterprise adoption is clustering around several use cases:
Content Generation
Marketing, communications, documentation:
- Draft creation with human review
- Personalisation at scale
- Translation and localisation
- Technical writing assistance
Relatively lower risk with appropriate review processes.
Code Assistance
Developer productivity:
- GitHub Copilot seeing significant adoption
- Code explanation and documentation
- Test generation
- Debugging assistance
Meaningful productivity gains reported by early adopters.
Knowledge Work Augmentation
Research, analysis, summarisation:
- Document analysis and synthesis
- Research assistance
- Meeting summarisation
- Email drafting
High potential value, requires careful governance.
Customer Interaction
Support and engagement:
- Enhanced chatbots
- Agent assistance
- Response drafting
- Sentiment analysis
Customer-facing applications require highest care.
Strategic Framework
Assess the Opportunity
Where Can AI Create Value?
Map your organisation’s activities against AI capabilities:
High Potential
- High-volume content creation
- Repetitive knowledge work
- Code development
- Customer support scaling
Moderate Potential
- Complex analysis and research
- Strategic planning support
- Creative ideation
- Training and education
Lower Potential (Currently)
- High-stakes decisions
- Regulated processes
- Novel problem solving
- Relationship-dependent work
Quantify the Prize
Estimate value for priority use cases:
- Time savings (hours × cost)
- Quality improvements
- Scalability enabled
- New capabilities unlocked
This justifies investment and helps prioritise.
Understand the Risks
Data Security
Information entered into AI systems:
- Where is it processed?
- Who can access it?
- Is it used for training?
- What’s the retention policy?
Azure OpenAI provides enterprise controls. Public ChatGPT does not.
Output Quality
AI systems hallucinate—generate plausible but incorrect information:
- Factual errors
- Fabricated citations
- Outdated information
- Logical inconsistencies
Human review remains essential for anything consequential.
Intellectual Property
Unclear legal landscape:
- Who owns AI-generated content?
- What about training data copyright?
- How do you protect proprietary information?
- What are disclosure obligations?
Legal guidance is essential. Standards are still emerging.
Regulatory Compliance

Depending on industry:
- Financial services AI requirements
- Healthcare information protection
- Employment law considerations
- Data protection regulations
Compliance teams must be involved from the start.
Reputational Risk
AI failures can be public and embarrassing:
- Incorrect information to customers
- Biased outputs
- Brand voice inconsistency
- Privacy violations
Start with lower-risk internal use cases.
Build Governance
Policy Framework
Establish clear policies covering:
- Approved tools and platforms
- Permitted use cases
- Prohibited uses
- Data handling requirements
- Review and approval processes
Policies should enable responsible use, not simply prohibit.
Technical Controls
Implement guardrails:
- Enterprise AI platforms (not consumer tools)
- Access management
- Usage monitoring
- Output logging
- Data loss prevention integration
Human Oversight
Define review requirements:
- What requires human review?
- Who is qualified to review?
- What’s the escalation path?
- How is quality assured?
Training and Enablement
Prepare your workforce:
- What AI is and isn’t
- How to use it effectively
- What the risks are
- How to comply with policies
Pilot Strategically
Select Initial Use Cases
Choose pilots that are:
- High value (demonstrates potential)
- Lower risk (manageable if problems occur)
- Measurable (can prove success)
- Representative (learnings apply broadly)
Define Success Criteria
Be specific about what you’re measuring:
- Productivity improvement (quantified)
- Quality maintenance or improvement
- User satisfaction
- Risk incidents
- Cost vs value
Learn and Iterate
Pilots should generate insights:
- What works well?
- What challenges emerged?
- What governance adjustments needed?
- What training gaps exist?
Document learnings before expanding.
Implementation Considerations
Platform Selection
Enterprise Requirements
Evaluate platforms against:
- Security certifications (SOC 2, ISO 27001)
- Data handling commitments
- Virtual network support
- Access controls
- Audit logging
- Support availability
Current Recommendation
For most enterprises today, Azure OpenAI Service provides the best balance of capability and enterprise controls. It offers GPT-4 access with Azure’s security infrastructure, compliance certifications, and integration capabilities.
Google’s offerings are maturing quickly. AWS Bedrock, when generally available, will provide another strong option. Evaluate alternatives as they develop.
Integration Patterns
API Integration
For custom applications:
- Embed AI capabilities in existing workflows
- Control the user experience
- Implement specific guardrails
- Integrate with enterprise systems
Requires development investment but provides most control.
Copilot-Style Integration
AI assistance within existing tools:
- GitHub Copilot for developers
- Microsoft 365 Copilot (coming)
- Third-party integrations
Lower development effort, less customisation.
Standalone Applications
Purpose-built AI applications:
- ChatGPT Enterprise (when available)
- Specialised AI tools
- Vendor applications with AI features
Fastest deployment, least integration.
Cost Management
Understand the Pricing
AI services typically charge by:
- Tokens processed (input and output)
- API calls
- Compute time
- Model tier (GPT-4 vs GPT-3.5)
Costs can grow quickly with adoption.
Optimise Usage
Manage costs through:
- Prompt engineering (shorter prompts)
- Model selection (use GPT-3.5 where sufficient)
- Caching common responses
- Rate limiting
- Usage monitoring and alerts
Budget Appropriately
Plan for:
- Pilot costs
- Scaled deployment costs
- Experimentation overhead
- Training and change management
Organisational Readiness
Skills and Capabilities
What You’ll Need
New capabilities required:
- Prompt engineering
- AI application development
- AI governance and ethics
- Vendor management for AI platforms
Build vs Buy
Decide how to acquire:
- Train existing staff
- Hire specialists
- Engage consultants
- Partner with vendors
A hybrid approach typically works best.
Change Management
Cultural Shift
AI adoption requires mindset changes:
- From executing to reviewing
- From creating to curating
- From individual to augmented productivity
Some employees will embrace this; others will resist.
Communication
Be clear about:
- Why you’re adopting AI
- What it means for roles
- What support is available
- How success will be measured
Address concerns honestly.
Operating Model
Centre of Excellence
Consider a central team to:
- Define standards and patterns
- Evaluate and approve tools
- Support adoption
- Monitor usage and outcomes
- Share learnings
Federated Execution
Enable business units to:
- Identify use cases
- Implement within guidelines
- Measure their outcomes
- Contribute learnings
Balance central governance with distributed innovation.
Looking Ahead
Near-Term Evolution
Expect in the coming months:
- Model capabilities improving rapidly
- Enterprise offerings maturing
- Pricing becoming more competitive
- Best practices solidifying
- Regulatory clarity emerging
The landscape will look different in six months.
Strategic Positioning
Organisations should:
- Build AI fluency across the workforce
- Establish governance frameworks now
- Pilot to learn, not just to deploy
- Monitor competitive developments
- Prepare for regulatory requirements
The goal is not to be first, but to be ready.
Conclusion
Generative AI represents a genuine technological shift. The productivity implications for knowledge work are substantial. The risks are real but manageable with appropriate governance.
The CTOs who will succeed are those who move beyond either hype or fear toward pragmatic, governed adoption. Start with clear strategy. Build appropriate controls. Pilot carefully. Learn continuously.
The organisations that build AI capability now will have advantages that compound over time. Those that delay too long will find themselves playing catch-up. The window for strategic positioning is now.
Sources
- OpenAI. (2023). GPT-4 Technical Report. https://openai.com/research/gpt-4
- Microsoft. (2023). Azure OpenAI Service Documentation. https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cognitive-services/openai/
- McKinsey Global Institute. (2023). The Economic Potential of Generative AI. McKinsey & Company.
- Gartner. (2023). Emerging Tech: Generative AI Impact Radar. Gartner Research.
Strategic guidance for enterprise technology leaders navigating the AI transformation.