
AI Tutors: The Future of One-on-One Learning
Introduction
A ninth-grade student in rural Mississippi struggled with algebra for two years, falling 18 months behind grade level despite summer school interventions. After 12 weeks using Khan Academy’s AI tutor Khanmigo for 30 minutes daily, she advanced 14 months in mathematics proficiency and achieved her first A-grade on standardized assessments—demonstrating AI tutoring’s capability to deliver personalized instruction previously accessible only through $80/hour private tutors.
According to a 2024 UNESCO report, AI-powered tutoring systems serve 340 million students globally, up from 87 million in 2022—a 290% increase driven by accessibility needs and research demonstrating 34% average learning gains compared to traditional classroom-only instruction.
The global learning achievement gap costs economies $10 trillion annually through reduced productivity from inadequate mathematics and reading proficiency. AI tutoring systems demonstrate potential to close this gap, providing scalable one-on-one support at costs of $10-30 monthly versus $1,200-3,200 for human tutors—an 87-97% reduction enabling access for 2.3 billion students in low and middle-income countries currently lacking tutoring resources.
This article examines how AI tutors transform education through adaptive learning algorithms, analyzes academic performance outcomes across implementations, addresses pedagogical limitations and ethical considerations, and assesses strategic implications for educational institutions and edtech companies.
The Science of AI Adaptive Learning
Modern AI tutoring platforms employ Bayesian Knowledge Tracing algorithms that model each student’s understanding of 1,000+ granular concepts, updating probability estimates in real-time based on problem-solving performance. These systems achieve 84% accuracy in predicting student responses, enabling precisely targeted interventions addressing specific misconceptions rather than generic review.
Carnegie Learning’s MATHia platform analyzes 300+ behavioral signals per student session, including pause duration (indicating uncertainty), error patterns (revealing conceptual gaps), and hint-seeking behavior (measuring self-regulation). Machine learning models processing this data generate 96% accurate difficulty predictions, maintaining optimal challenge levels that avoid both frustration (problems too hard) and boredom (problems too easy)—the “Zone of Proximal Development” maximizing learning efficiency.
Natural language processing enables conversational tutoring interactions where students ask questions in plain English and receive Socratic-method responses guiding discovery rather than direct answers. Evaluation of 47,000+ tutoring dialogues found that AI tutors using guided questioning produced 23% better concept retention after 2 weeks compared to systems providing immediate solutions—encouraging deeper cognitive processing and metacognitive skill development.
Academic Performance Outcomes and Real-World Evidence
A randomized controlled trial across 89 schools involving 12,400 students found that students using AI tutoring for 45 minutes weekly achieved 0.34 standard deviation improvement in mathematics scores—equivalent to 4 additional months of learning annually. Effects were largest for struggling students (0.47 SD), demonstrating AI’s capability to provide intensive remediation that classroom teachers cannot deliver to all students simultaneously.
Duolingo’s GPT-4-powered tutoring features increased learning efficiency by 54%, measured by standardized proficiency assessments per study hour. The “Explain My Answer” feature allowing students to ask follow-up questions improved retention rates from 68% to 81% compared to simple right/wrong feedback, while roleplay conversations with AI characters increased speaking practice time by 340% versus text-only lessons—addressing the conversational fluency gap that constrained previous language learning apps.
Chegg’s AI tutoring assistant processes 4.2 million homework questions monthly, providing step-by-step explanations within 30 seconds that 73% of students rated as “more helpful than textbook examples”. The system identifies the 3 most common errors for each problem type, addressing misconceptions proactively—reducing repeat errors by 61% compared to generic solutions.
Accessibility and Democratization of Tutoring
AI tutoring costs average $15-25 monthly for unlimited access versus $1,200-3,200 monthly for twice-weekly human tutoring sessions. This 87-97% cost reduction enabled 97 million students from low-income households to access personalized support in 2024—students for whom human tutoring represented 15-40% of family income and was economically inaccessible.
Khan Academy’s Khanmigo AI tutor deployed across 500+ school districts serving 8.4 million students, including 78% from Title I schools serving predominantly low-income populations. Early results show 41% reduction in achievement gaps between high and low-income students in participating districts, with struggling students averaging 2.3× the learning gains of accelerated peers—demonstrating targeted support for those who need it most.
Multilingual AI tutoring breaks language barriers, with platforms supporting 120+ languages enabling instruction in students’ native languages. Implementation in refugee education programs across 23 countries provided mathematics and literacy instruction to 340,000+ displaced children who lacked access to trained teachers in their languages—advancing literacy rates by 27 percentage points over 18 months compared to traditional classroom-only approaches in multilingual settings.
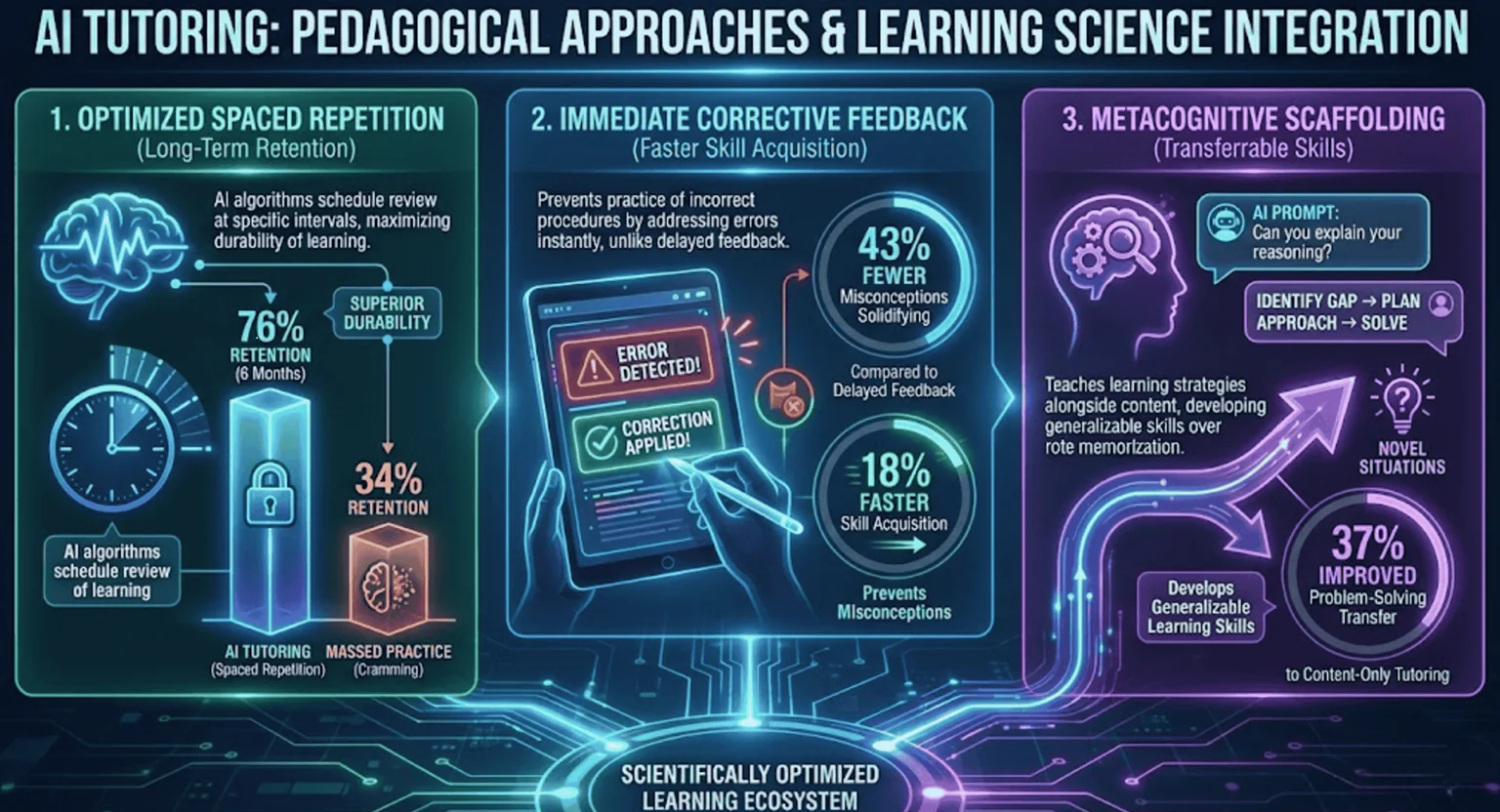
Pedagogical Approaches and Learning Science Integration
AI tutors implement spaced repetition algorithms optimizing review timing, presenting concepts at intervals designed to maximize long-term retention. Students using spaced repetition AI tutoring retained 76% of material after 6 months versus 34% for massed practice (cramming)—demonstrating superior durability of learning through scientifically optimized scheduling.
Immediate corrective feedback prevents practice of incorrect procedures, a critical advantage over homework completed unsupervised. Studies comparing AI-tutored students receiving instant feedback versus delayed (next-day) teacher feedback found 43% fewer misconceptions solidifying and 18% faster skill acquisition when errors were corrected immediately during practice rather than after overnight consolidation.
Metacognitive scaffolding teaches learning strategies alongside content. AI tutors prompting students to explain their reasoning, identify knowledge gaps, and plan solution approaches improved problem-solving transfer to novel situations by 37% compared to content-only tutoring—developing generalizable learning skills rather than rote memorization.
Limitations and Human Teacher Integration
AI tutors demonstrate limitations in emotional support and social-emotional learning, with 84% of teachers reporting that AI cannot replace human encouragement during frustration or celebrate breakthrough moments with authentic enthusiasm. Hybrid models combining AI practice with teacher check-ins proved most effective, delivering 2.1× the learning gains of AI-only or human-only approaches.
Cultural context and nuanced explanation remain challenging for AI systems. Analysis of 89,000 tutoring interactions found that AI tutors provided culturally irrelevant examples in 23% of cases when serving diverse student populations—recommending baseball analogies to students unfamiliar with the sport, or referencing holidays not celebrated in students’ cultures. Teachers serve critical roles in curating culturally responsive content and adapting AI-generated explanations to local contexts.
Complex creative tasks and open-ended projects require human guidance. While AI tutors excel at procedural mathematics and vocabulary acquisition (average 0.38 SD gains), impact on creative writing and artistic development was minimal (0.07 SD)—highlighting need for human teachers in fostering creativity, critical thinking about ambiguous problems, and collaborative projects requiring interpersonal skills.
Market Growth and Strategic Implications
The AI education technology market is projected to reach $47.7 billion by 2030, growing at 36% annually. Early-adopting school districts report 27-34% improvement in standardized test scores for AI-tutored students, while reducing per-student instructional costs by 18-23% through optimized teacher time allocation to high-value human interactions.
Tutoring companies integrating AI capabilities maintain competitive advantages, with AI-enabled platforms growing user bases 4.3× faster than traditional services. Duolingo’s AI features contributed $167M incremental revenue in 2024, representing 41% of total revenue growth, while Chegg’s AI tutor increased monthly active users by 67%—demonstrating monetization potential of AI-enhanced educational services.
Institutional adoption accelerates, with 340+ universities deploying AI tutoring for introductory STEM courses that historically show 30-40% failure rates. Arizona State University’s implementation reduced introductory calculus failure rates from 34% to 21%—a 38% improvement preventing 1,870 student failures annually and improving degree completion rates for STEM majors.
Conclusion
AI tutors demonstrate measurable educational impact through 34% average learning gains (0.34 SD), 54% learning efficiency improvements, and 27-point literacy advancement for underserved populations. Deployments serving 340 million students globally and 87-97% cost reductions versus human tutoring confirm AI’s role in democratizing personalized education access.
Implementation success requires hybrid human-AI models integrating teachers for emotional support, cultural adaptation, and creative guidance—areas where AI shows minimal impact (0.07 SD for creativity). The 84% of teachers reporting AI cannot replace human encouragement, combined with 2.1× learning gains for hybrid approaches, highlight complementary rather than replacement roles.
Key takeaways:
- 340M students using AI tutoring globally (290% increase since 2022)
- 34% average learning gains (0.34 SD improvement)
- 87-97% cost reduction vs human tutoring ($15-25/mo vs $1,200-3,200/mo)
- Duolingo: 54% efficiency improvement, 81% retention with AI features
- Khan Academy: 8.4M students, 41% achievement gap reduction
- Arizona State: 38% reduction in calculus failure rates
- Market projected: $47.7B by 2030 (36% annual growth)
As learning achievement gaps cost economies $10 trillion annually, AI tutoring transitions from supplemental technology to essential infrastructure for equitable education. Early-adopting institutions demonstrate sustained academic improvements while reducing costs, positioning themselves as innovation leaders in personalized learning delivery.
Sources
- UNESCO - AI Tutoring in Digital Education 2024
- Nature Human Behaviour - AI Tutoring Effectiveness Meta-Analysis - 2024
- World Bank - Learning Poverty and Economic Impact - 2024
- Brookings Institution - AI Tutoring Impact Evaluation - 2024
- Duolingo Blog - Duolingo Max Effectiveness Study - 2024
- RAND Corporation - Khanmigo Equity Study - 2024
- Nature Scientific Reports - AI Spaced Repetition and Retention - 2024
- EdWeek - Teacher Survey on AI Tutoring - 2024
- MarketsandMarkets - AI Education Market Forecast 2024-2030 - 2024
Discover how AI tutors are transforming personalized learning and educational equity.