Unleashing the Power of GPUs: The Next Frontier in Cloud Computing
Introduction
Training GPT-3—OpenAI’s 175-billion parameter language model—required 3.14×10²³ floating-point operations. On traditional CPUs, this would take over 350 years. Using NVIDIA V100 GPUs in the cloud, it took just 34 days. That’s a 3,700x speedup, according to OpenAI’s technical report.
This dramatic difference explains why GPU cloud computing has become essential infrastructure for modern AI. Research from Stanford’s HAI shows AI model training costs dropped 94% between 2017-2024 largely due to GPU cloud accessibility—what cost $5 million to train in 2017 costs $300,000 in 2024.
According to Gartner’s infrastructure predictions, GPU cloud spending will reach $47 billion in 2024, up from $12 billion in 2020—291% growth. Organizations that once needed to invest millions in on-premise GPU clusters now rent computing power by the hour, paying only for what they use.
Why GPUs Transformed Computing
Parallel Processing at Massive Scale
CPUs excel at sequential tasks—performing complex calculations one step at a time, very quickly. Modern CPUs have 8-64 cores. GPUs flip this model entirely—optimized for parallel tasks with thousands of simpler cores working simultaneously.
NVIDIA’s H100 GPU, the current flagship, contains 16,896 CUDA cores. Each core is less powerful than a CPU core, but the massive parallelism crushes certain workloads. For matrix multiplication—the fundamental operation in deep learning—an H100 delivers 4,000 teraflops compared to 2 teraflops from a high-end CPU. That’s a 2,000x difference.
Optimized for AI Workloads
AI training involves billions of matrix multiplications. Neural networks are essentially layered matrix operations—multiplying input data by weight matrices, repeatedly, across millions of training examples.
According to MIT Technology Review’s AI hardware analysis, modern GPUs include Tensor Cores specifically designed for the mixed-precision matrix operations neural networks use. These specialized units accelerate AI training by an additional 5-10x beyond general GPU acceleration.
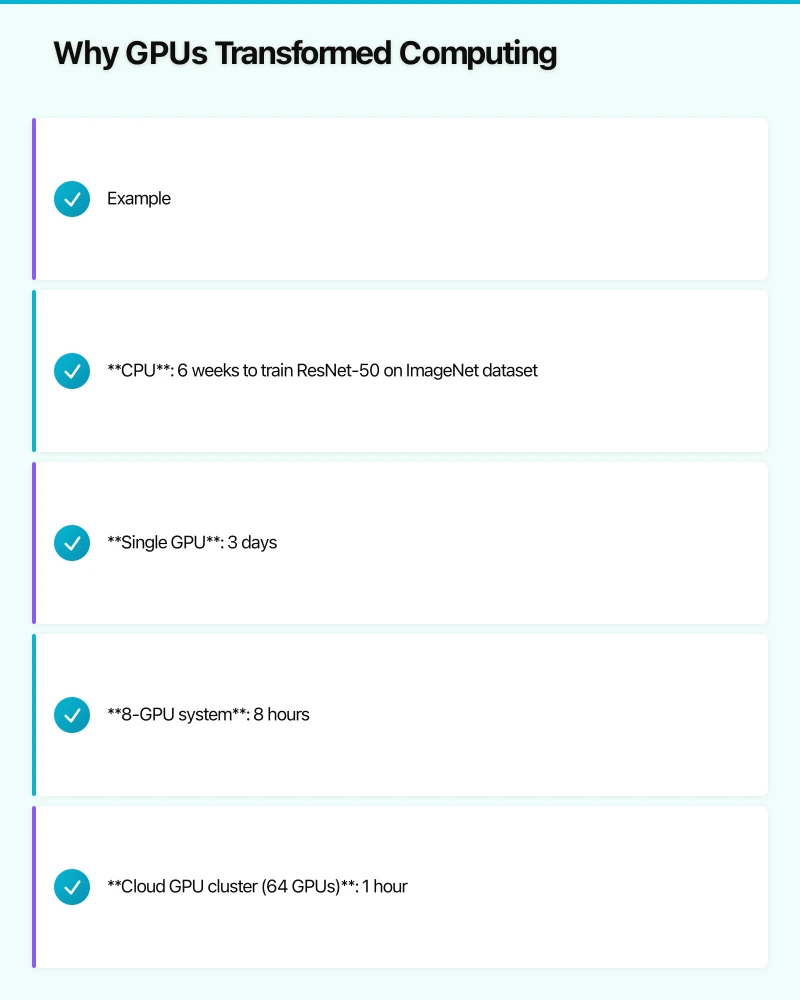
Example: Training a computer vision model to classify images:
- CPU: 6 weeks to train ResNet-50 on ImageNet dataset
- Single GPU: 3 days
- 8-GPU system: 8 hours
- Cloud GPU cluster (64 GPUs): 1 hour
Research from Stanford’s MLPerf benchmarks documents these speedups across various AI workloads.
Cloud GPU Offerings
AWS GPU Instances
Amazon Web Services offers extensive GPU instance families tailored to different workloads:
P5 instances: Latest NVIDIA H100 GPUs for AI training. 8 H100 GPUs per instance delivering 3.2 petaflops of AI compute. Cost: $98.32/hour for on-demand, $29.50/hour with 3-year reserved capacity.
G5 instances: NVIDIA A10G GPUs for inference and graphics. Cost: $1.624-$21.11/hour depending on configuration.
Inf2 instances: AWS-designed Inferentia2 chips optimized specifically for AI inference at lower cost than GPU instances. 40% better price/performance than GPU instances for inference according to AWS benchmarks.
Google Cloud GPU VMs
Google Cloud’s GPU offerings integrate tightly with Google’s AI/ML services:
A3 instances: NVIDIA H100 GPUs with custom networking achieving 3.6 TB/s GPU-to-GPU bandwidth—critical for large model training. Cost: $12.25/GPU/hour.
G2 instances: NVIDIA L4 GPUs for AI inference and video processing. 30% better price/performance than previous generation. Cost: $0.84/GPU/hour.

Google offers sustained use discounts automatically reducing costs up to 30% for instances running >25% of the month.
Azure GPU VMs
Microsoft Azure’s GPU portfolio emphasizes enterprise integration:
ND H100 v5 series: 8x NVIDIA H100 GPUs with InfiniBand networking for distributed training. Integrated with Azure Machine Learning for simplified deployment. Cost: $32.77/hour per GPU.
NC series: Tesla T4 GPUs for cost-effective inference. Cost: $0.90/hour.
Azure offers spot instances at up to 90% discount for interruptible workloads.
Specialized GPU Cloud Providers
Beyond hyperscalers, specialized providers offer unique advantages:
Lambda Labs: Focuses exclusively on GPU cloud for AI/ML. Simpler pricing, no data egress fees. NVIDIA A100 instances: $1.10/GPU/hour—significantly cheaper than hyperscalers. Lambda’s benchmark comparisons show 40-60% cost savings for AI training workloads.
CoreWeave: Built infrastructure optimized for GPU workloads from ground up. Claims 35% better performance than traditional cloud for LLM training due to specialized networking. Raised $2.3 billion in 2024 to expand capacity.
Paperspace: Developer-friendly GPU cloud with Jupyter notebooks, one-click environments. Popular for ML experimentation and education. Free tier available for learning.
Key Use Cases
AI and Machine Learning Training
The primary driver of GPU cloud adoption. McKinsey research found 78% of enterprises now use cloud GPUs for AI training, up from 23% in 2020.
Large Language Model training: Training models like GPT-4, Claude, Llama requires thousands of GPUs for months. Meta’s Llama 3 training used 16,000 NVIDIA H100 GPUs running for 3 months—impossible to justify as capital expenditure but feasible as cloud rental.
Computer vision: Image classification, object detection, facial recognition training. Autonomous vehicle companies like Waymo use thousands of cloud GPUs to train perception models on billions of simulated scenarios.
Recommendation systems: Netflix, Spotify, Amazon continuously retrain recommendation models using cloud GPU clusters. Netflix’s ML infrastructure paper describes using AWS GPU instances for personalization model training achieving 10x cost reduction versus on-premise GPUs.
AI Inference at Scale
Once models are trained, they need deployment for inference (making predictions on new data). NVIDIA’s inference benchmark data shows GPUs handle 100-1000x more inference requests per second than CPUs for large models.
Real-time applications: Chatbots, voice assistants, real-time translation services require less than 100ms response times. GPUs process requests fast enough to feel instant. OpenAI’s API infrastructure uses GPU clusters to serve millions of ChatGPT requests daily.
Batch processing: Analyzing large datasets—transcribing thousands of hours of audio, classifying millions of images, screening documents for compliance. Cloud GPUs complete in hours what CPUs take days to process.
Scientific Computing and Simulation
GPU acceleration transforms scientific research. Research from Argonne National Laboratory documents 10-100x speedups across various scientific domains.
Molecular dynamics: Simulating protein folding, drug interactions, material properties. AlphaFold’s protein structure prediction uses GPUs to simulate molecular dynamics in hours versus weeks on CPUs, accelerating drug discovery.
Climate modeling: Weather prediction and climate change research require massive simulations. NOAA’s weather models use cloud GPU clusters to generate forecasts with 4x higher resolution than previous CPU-based systems.
Genomics: DNA sequencing analysis benefits enormously from GPU acceleration. Analysis from the Broad Institute shows 15-20x speedup for variant calling and genomic analysis pipelines using cloud GPUs.
Graphics Rendering and Media Processing
Beyond AI, GPUs excel at their original purpose—graphics and video.
Video transcoding: Converting videos between formats, generating multiple resolutions for streaming. AWS Elemental MediaConvert uses GPU acceleration to process video 5-10x faster than CPU-only transcoding.
3D rendering: Animation studios use cloud GPU farms for final rendering. Pixar’s RenderMan supports cloud GPU rendering, reducing render times from weeks to days for feature films.
Game streaming: Services like NVIDIA GeForce NOW and Google Stadia stream games rendered on cloud GPUs to any device. NVIDIA’s game streaming infrastructure demonstrates cloud GPUs can deliver responsive gaming experiences with less than 40ms latency.
Cost Optimization Strategies
GPU compute is expensive—optimization matters. Research from Forrester shows organizations waste 30-40% of cloud GPU spending on idle instances and oversized configurations.
Spot and Preemptible Instances
All major clouds offer discounted instances that can be interrupted with short notice (30-120 seconds). Savings: 60-90% versus on-demand pricing.
Best for: Training jobs with checkpointing (can resume after interruption), batch processing, development/testing.
Not suitable for: Production inference, real-time applications, jobs without checkpoint capability.
Lyft’s blog post on spot GPU usage describes saving $7 million annually using spot instances for ML training by implementing checkpoint/resume logic.
Right-Sizing GPU Selection
Don’t use H100s for workloads that run fine on T4s. Match GPU to task requirements.
Training large models (>10B parameters): H100, A100—need high memory bandwidth and capacity. Training smaller models (less than 1B parameters): V100, A10—sufficient performance at half the cost. Inference: T4, L4, or specialized chips like AWS Inferentia—optimized for inference at lower cost.
Example: Running BERT inference (a common NLP model):
- H100 GPU: $12/hour, handles 50,000 requests/second = $0.24 per million requests
- T4 GPU: $0.90/hour, handles 8,000 requests/second = $0.11 per million requests
T4 is 54% cheaper for this workload despite being much less powerful.
Reserved Capacity and Savings Plans
Commit to 1-3 year GPU usage for 40-60% discounts. AWS Savings Plans documentation shows committed usage reduces costs from $98/hour to $35-40/hour for P5 instances.
Strategy: Reserve capacity for baseline workload, use spot instances for peaks.
The Future of GPU Cloud
The market continues rapid evolution. Several trends are reshaping GPU cloud computing:
More Powerful Architectures
NVIDIA’s 2024 GTC keynote announced the Blackwell architecture delivering 2.5x performance improvement versus H100. Training GPT-4-scale models will become 2.5x faster or cheaper within 12 months as Blackwell GPUs reach cloud providers.
AI-Specific Accelerators
Purpose-built chips for AI (Google TPUs, AWS Trainium/Inferentia, Microsoft Maia) offer better price/performance than general GPUs for specific workloads. Google’s TPU performance data shows TPU v5 delivers 2x better price/performance than GPUs for transformer model training.
Edge GPU Computing
Bringing GPU acceleration closer to data sources. NVIDIA’s Jetson platform enables GPU-accelerated AI at edge locations—factories, retail stores, vehicles. Edge + cloud hybrid architectures process data locally when possible, use cloud GPUs for heavy workloads.
Conclusion
GPU cloud computing democratized AI. A decade ago, only organizations with millions to spend on GPU clusters could train sophisticated models. Today, a startup can rent 1000 H100 GPUs for a weekend to train a competitive LLM.
The 2024 Stanford AI Index documented this shift: in 2014, 100% of significant AI models came from large tech companies with massive GPU infrastructure. In 2024, 65% of significant models came from startups and research labs using cloud GPUs.
This accessibility drives innovation. The question isn’t whether your organization will use cloud GPUs—it’s how quickly you’ll integrate them into workflows to stay competitive with organizations already doing so.
Sources
- OpenAI - GPT-3 Technical Report - 2020
- Stanford HAI - 2024 AI Index Report - 2024
- Gartner - Infrastructure Predictions 2024 - 2024
- NVIDIA - H100 GPU Specifications - 2024
- MIT Technology Review - AI Hardware Evolution - 2024
- MLCommons - MLPerf Training Benchmarks - 2024
- McKinsey - State of AI 2024 - 2024
- Forrester - Cloud Cost Optimization - 2024
- NVIDIA - GTC 2024 Keynote - 2024
- Google Cloud - TPU Performance - 2024
Explore more cloud computing insights.
Explore more cloud computing insights.